The recovery and «non-wear» effects implementation with the repair-restoration compounds becomes possible due to the initialization of the friction surfaces modification process.
Conditionally imagine the process of modification of friction surfaces as a result of interaction with the RRC:
 1. Figure 1 shows the interaction of friction surfaces of mating members accompanied by the significant amount of heat energy liberation that accelerates the processes of surface wear and destruction of lubricants. |
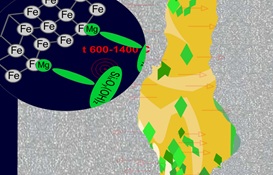 2. Figure 2 shows the process of initialization by repair-restoration compounds of the formation of crystalline structures having a single framework with a more volumetric lattice with a base metal, which provides, among other things, compensation for the wear that has occurred. |
 3. Figure 3 shows the newly formed blankets, the amount of which is controlled by the friction system itself – the levelling of the microrelief leads to a decrease in the release of contact energy, and the further growth of the protective layer stops (RRC do not interact with surfaces where there is no friction). The obtained protective layers have mechanical properties superior to the material of the substrates on which they were formed, improving the working conditions of friction pairs. Modification of surfaces increases the true areas of contact spots, which reduces specific pressures and friction and, as a result, the intensity of wear. This leads to a significant increase in the life of the friction pair and the life of the lubricants used, extending the period of their normal operation. |
Materials brought here are the fragments of works carried out with the purpose of comparative research of the friction surfaces and studying of theirs physical, mechanical and tribological characteristics.
Comparative studying of friction surfaces before and after they have been treated with RRC was carried out by research organizations of different countries with application of different methods.
This section contains some photographs and some of the graphic materials that are quotes from different research works.
More detailed information may be brought upon separate request.
Quotes from research work of «Odessa National Maritime University» («Scientific Research Institute of Basic and applied Researches»)
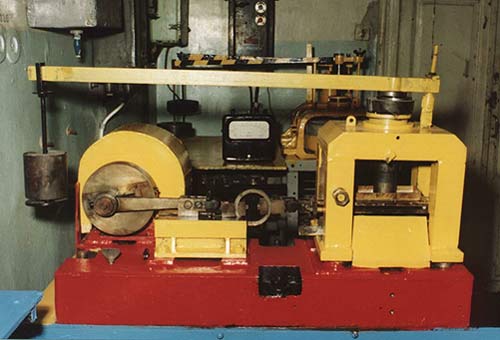
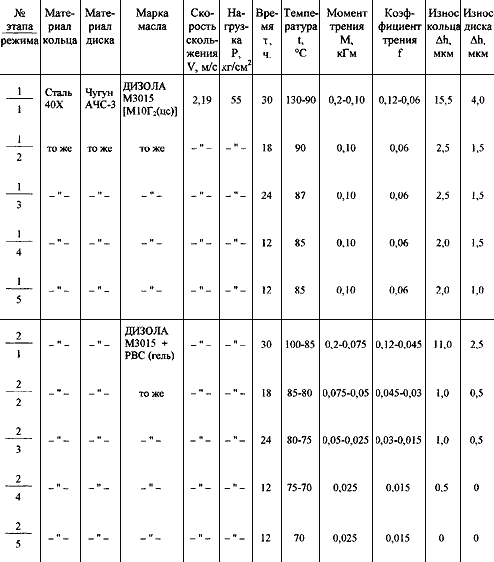
Quotes from the researches carried out on the base of Zabajkal’skij Railway Transport Institute, Chita. Definition of sliding friction coefficients of the shaft-to-bearing shell pair were carried out with a method developed in the Moscow State Technical University n.a. N. E. Bauman.
Quote from scientific research work Saint-Petersburg State Polytechnical University Stand tests of gasoline engine manufactured by ZMZ.
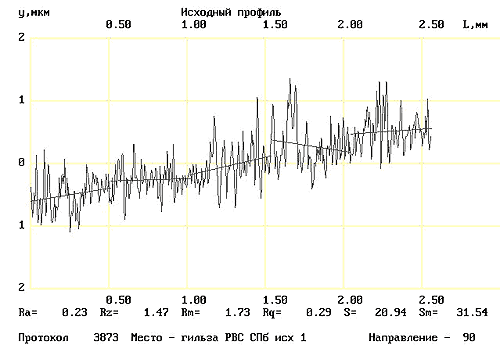
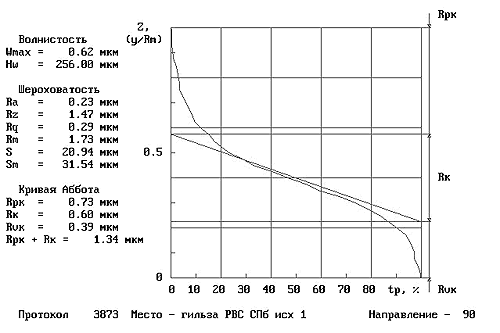
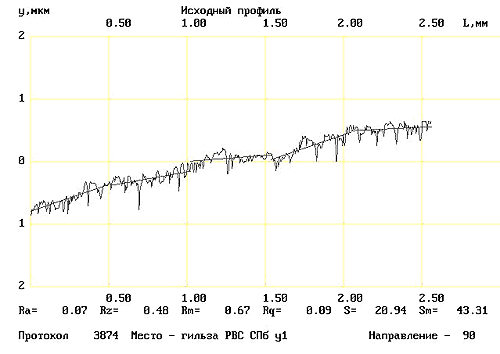
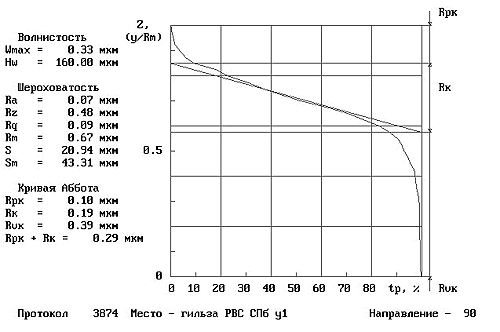
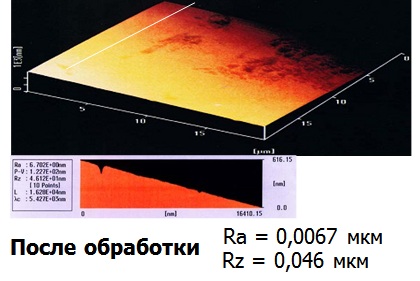
The materials of Waseda University of Tokyo, depicting the friction surfaces BEFORE (Fig. 11) and AFTER (Fig. 12) of the use of RRC, confirm the result of the interaction of RRC and friction surfaces:
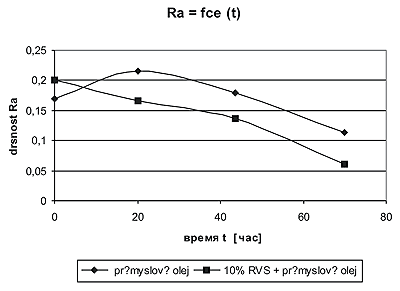
– surface roughness reduction is visualized, instrumental control recorded the improvement of characteristics by an order of magnitude;
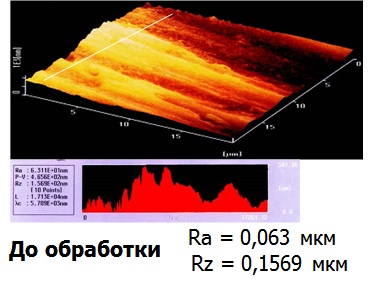
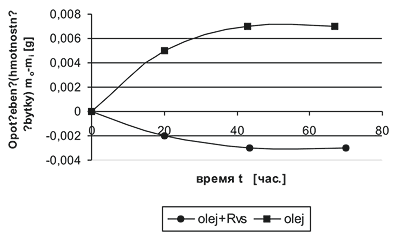
– along the axis of ordinates partial compensation of the wear occurred is represented.
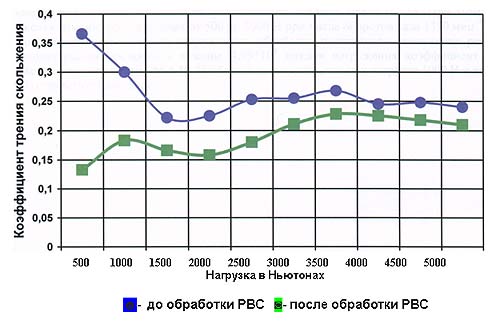
Quote from the research carried out in Finland. Determination of tribological properties of wear surfaces: metal-metal (in oil) and metal-metal (in oil + RRC).